Welcome to the Ultimate Guide on Managing Your Finances: Discover the power of Debt to Income Ratio Calculator( DTI Ratio Calculator).We’ll unveil the benefits and usage of this essential financial instrument DTI Calculator, empowering you to make well-informed decisions when borrowing money or managing your debts. Join us as we explore the fascinating realm of debt-to-income calculations and take control of your financial future!
Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio Calculator
Results
- Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio:
- Total Income/Year:
- Total Income/Month:
- Total Debt/Year:
- Total Debt/Month:
What is a Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Debt-to-income ratio is a critical financial metric used by lenders to determine an individual’s creditworthiness. It is the percentage of your monthly income that goes towards paying off your debts, including credit card balances, mortgage payments, car loans, and any other recurring debt obligations.
Understanding your debt-to-income ratio
It is crucial because it provides insight into your financial health and your ability to take on additional debt. A low debt-to-income ratio indicates that you have a good handle on your finances and can comfortably manage your debt obligations. Conversely, a high debt-to-income ratio can be a red flag for lenders, indicating that you may struggle to keep up with your debt payments.
Calculating your debt-to-income ratio
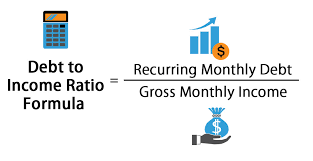
It is relatively straightforward. To do so, you’ll need to add up all of your monthly debt payments, including your rent or mortgage payment, car payment, credit card payments, and any other recurring debt obligations. Then, divide this total by your monthly gross income, which is your income before taxes and other deductions.
For example, if your monthly debt payments total $1,500, and your gross monthly income is $5,000, your debt-to-income ratio would be 30% ($1,500 / $5,000 x 100).
The general rule of thumb is that your debt-to-income ratio should be no more than 43%. However, some lenders may have different requirements, so it’s always best to check with them directly.
It’s important to note that your debt-to-income ratio is not the only factor lenders consider when assessing your creditworthiness. They also consider your credit score, employment history, and other financial factors. However, having a low debt-to-income ratio can go a long way in helping you secure favorable loan terms and interest rates.
In conclusion, understanding your debt-to-income ratio is crucial for maintaining good financial health and securing credit when you need it. By keeping your debt-to-income ratio low, you can demonstrate your ability to manage your finances responsibly and improve your chances of getting approved for loans and credit cards with favorable terms.
Why is it Important?
Debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a critical financial metric used by lenders to evaluate an individual’s ability to take on additional debt. It compares an individual’s monthly debt payments to their monthly income, providing lenders with insight into their overall financial health and creditworthiness.
DTI is important for several reasons
First, it helps lenders assess an individual’s ability to make their monthly payments on time. If an individual’s DTI is too high, they may struggle to keep up with their debt obligations, which can result in missed payments, late fees, and damage to their credit score.
Second, DTI is a useful tool for individuals to evaluate their own financial health. By calculating their DTI, individuals can get a clear picture of their current debt load and assess their ability to take on additional debt. This can help them make informed decisions about whether to take out a loan or credit card, and how much debt they can comfortably afford to take on.
Third, DTI is an important factor in determining an individual’s eligibility for loans and credit cards. Lenders use DTI, along with other financial metrics such as credit score and employment history, to assess an individual’s creditworthiness and determine whether they are a good candidate for a loan or credit card. If an individual’s DTI is too high, they may be denied credit or offered unfavorable terms, such as higher interest rates or lower credit limits.
In summary, DTI is an important financial metric that provides lenders with insight into an individual’s ability to manage their debt obligations. It is also a useful tool for individuals to evaluate their own financial health and make informed decisions about taking on additional debt. By keeping their DTI low, individuals can improve their creditworthiness and increase their chances of getting approved for loans and credit cards with favorable terms.
What is Front-End Ratio and Back-End Ratio
When applying for a mortgage or other type of loan, lenders will evaluate your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) to determine your creditworthiness. DTI is calculated by dividing your monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income. However, there are two types of DTI that lenders use: front-end ratio and back-end ratio.
Front-end ratio
also known as housing ratio, is the percentage of your monthly income that goes towards housing expenses, such as your mortgage payment, property taxes, and homeowners insurance. To calculate your front-end ratio, divide your monthly housing expenses by your monthly gross income. Lenders typically prefer a front-end ratio of no more than 28%.
Back-end ratio
also known as total debt ratio, is the percentage of your monthly income that goes towards all of your debt obligations, including housing expenses, credit card payments, car payments, and any other recurring debt obligations. To calculate your back-end ratio, divide your total monthly debt payments by your monthly gross income. Lenders typically prefer a back-end ratio of no more than 36%.
It’s important to understand both front-end and back-end ratios because they provide lenders with different information about your ability to take on additional debt. Front-end ratio specifically focuses on your ability to manage housing expenses, while back-end ratio takes into account all of your debt obligations.
When applying for a mortgage, lenders will typically evaluate both front-end and back-end ratios to determine your creditworthiness. If your ratios are too high, you may be denied a mortgage or offered unfavorable terms, such as higher interest rates or a larger down payment.
In conclusion, front-end and back-end ratios are both important financial metrics used by lenders to evaluate an individual’s creditworthiness. Understanding these ratios and how they are calculated can help you make informed decisions about your finances and increase your chances of getting approved for a mortgage or other type of loan with favorable terms.
How to Lower Debt-to-Income Ratio
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a critical financial metric used by lenders to evaluate your creditworthiness. It compares your monthly debt payments to your monthly income, providing insight into your ability to manage your debt obligations. A high DTI can make it difficult to get approved for loans and credit cards with favorable terms, so it’s important to take steps to lower your ratio. Here are some tips for doing so:
Pay off your debts: One of the most effective ways to lower your DTI is to pay off your debts. Start by focusing on your high-interest debts first, such as credit card balances, and work your way down to your lower-interest debts. Paying off your debts will not only lower your DTI but also improve your credit score.
Increase your income: Another way to lower your DTI is to increase your income. Consider taking on a side hustle, asking for a raise, or looking for a higher-paying job. Increasing your income can help you pay off your debts faster and lower your DTI.
Refinance your debts: If you have high-interest debts, consider refinancing them to lower your interest rates and monthly payments. This can help you pay off your debts faster and lower your DTI.
Create a budget: Creating a budget can help you track your spending and identify areas where you can cut back. By reducing your expenses, you can free up more money to pay off your debts and lower your DTI.
Avoid taking on new debt: Avoid taking on new debt, such as credit cards or loans, until you have paid off your existing debts. Taking on new debt will only increase your DTI and make it harder to get approved for loans and credit cards in the future.
In conclusion, lowering your debt-to-income ratio is crucial for maintaining good financial health and securing credit when you need it. By paying off your debts, increasing your income, refinancing your debts, creating a budget, and avoiding new debt, you can lower your DTI and improve your creditworthiness. Remember, the lower your DTI, the better your chances of getting approved for loans and credit cards with favorable terms.
How to calculate debt to income ratio?
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to calculate your DTI:
Step 1: Add up your monthly debt payments To calculate your DTI, you’ll first need to add up all of your monthly debt payments. This includes your rent or mortgage payment, car payment, credit card payments, student loan payments, and any other recurring debt obligations.
Step 2: Determine your gross monthly income Your gross monthly income is your income before taxes and other deductions. This includes your salary, wages, tips, and any other sources of income you receive on a regular basis.
Step 3: Divide your monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income Once you have your total monthly debt payments and gross monthly income, divide your monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income. This will give you your debt to income ratio as a percentage.
For example, if your total monthly debt payments are $1,500, and your gross monthly income is $5,000, your DTI would be 30% ($1,500 / $5,000 x 100).
Step 4: Evaluate your DTI The general rule of thumb is that your DTI should be no more than 43%. However, some lenders may have different requirements, so it’s always best to check with them directly.
If your DTI is too high, it may be difficult to get approved for loans and credit cards with favorable terms. In this case, you may need to take steps to lower your DTI, such as paying off your debts, increasing your income, or refinancing your debts.
How to Use a DTI Calculator
Debt to Income Ratio (DTI) is a fundamental financial metric that plays a pivotal role in assessing your financial health and your ability to manage debt responsibly. Calculating your DTI is a straightforward process, and tools like the Debt to Income Ratio Calculator, DTI Ratio calculator, and DTI Calculator can assist you in this essential financial task.
In this article, we’ll delve into what DTI is, why it matters, and how to use a DTI calculator to evaluate your financial well-being.
What is Debt to Income Ratio (DTI)?
Debt to Income Ratio, commonly referred to as DTI, is a percentage that expresses the relationship between your monthly debt payments and your gross monthly income. It provides a clear picture of how much of your income goes toward repaying debts.
Your DTI is typically divided into two categories:
Front-end DTI: This includes your housing-related expenses, such as mortgage or rent payments, property taxes, and homeowners’ insurance.
Back-end DTI: This encompasses all your monthly debt obligations, including credit card payments, car loans, student loans, personal loans, and any other debts you may have.
Why Does DTI Matter?
DTI is a crucial metric for several reasons:
Lending Decisions: Lenders, such as banks and mortgage companies, often use DTI to determine your creditworthiness. A lower DTI indicates that you have more disposable income to cover new debts, making you a more attractive borrower.
Budgeting: Calculating your DTI helps you assess your financial health and understand how much of your income is allocated to debt payments. It can guide your budgeting efforts and help you make informed financial decisions.
Risk Management: A high DTI suggests that you may be overleveraged, making it difficult to manage your existing debts and potentially increasing your financial stress.
Using a DTI Calculator:
Calculating your DTI is relatively straightforward, especially when using a DTI Calculator. Here’s how to do it:
Gather Financial Information: Collect your monthly gross income and all your monthly debt payments.
Input Information: Open a DTI Calculator and input your gross monthly income, your housing expenses (front-end DTI), and your total monthly debt obligations (back-end DTI).
Get Your DTI: The calculator will provide you with your DTI as a percentage. The result is typically expressed in two forms: front-end and back-end DTI.
Interpret the Result: A lower DTI indicates that a smaller portion of your income is allocated to debt payments, which is generally seen as favorable.
Interpreting the Results:
- Good DTI: A DTI below 36% is generally considered healthy, suggesting that you have a manageable level of debt relative to your income.
- Moderate DTI: A DTI between 36% and 50% may be manageable but indicates that a significant portion of your income goes toward debt.
- High DTI: A DTI above 50% is a red flag, suggesting that you are heavily burdened by debt and may struggle to meet your financial obligations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a Debt to Income Ratio (DTI)?
- Debt to Income Ratio, or DTI, is a financial metric that measures the relationship between your monthly debt payments and your gross monthly income.
Why is DTI important?
- DTI is crucial because it helps assess your financial health and creditworthiness. It’s often used by lenders to make lending decisions and is a valuable tool for budgeting and managing debt.
What is a Debt to Income Ratio Calculator?
- A Debt to Income Ratio Calculator is a tool that helps you calculate your DTI. It simplifies the process by providing a clear DTI percentage, often categorized as front-end and back-end DTI.
How do I use a DTI Calculator?
- To use a DTI Calculator, gather information on your monthly gross income, housing expenses (front-end DTI), and all monthly debt obligations (back-end DTI). Input this data into the calculator, and it will provide your DTI as a percentage.
What is DTI Ratio calculator?
- “DTI Ratio calculator” is a similar term used to describe a calculator that helps you determine your Debt to Income Ratio. It performs the same function as a DTI Calculator.
Why should I pay attention to my DTI?
- Monitoring your DTI is essential to gauge your ability to manage your debts and to keep your financial health in check. A low DTI is generally desirable for better financial stability.
What is a good DTI ratio?
- A good DTI ratio is typically below 36%. It suggests that you have a manageable level of debt relative to your income.
What should I do if my DTI is high?
- If your DTI is high (above 50%), it’s a signal that you may be overburdened by debt. Consider creating a plan to reduce your debt, increase your income, or both to improve your financial situation.
How often should I check my DTI?
- It’s a good practice to check your DTI regularly, especially when considering major financial decisions or seeking loans. At a minimum, annual checks are recommended to stay on top of your financial health.
How can I improve my DTI?
- To improve your DTI, focus on reducing your debt, increasing your income, and being mindful of your financial obligations. Cutting unnecessary expenses and paying down debt are effective strategies.
Conclusion
The DTI Ratio Calculator is a powerful tool that can help you take control of your financial future by providing insights into your debt management capabilities. By understanding and monitoring your DTI ratio, you can make informed decisions and maintain good financial health. So, whether you’re planning to apply for a loan or seeking to improve your overall financial standing, be sure to leverage the power of the DTI Ratio Calculator to guide your journey towards financial success.
Legal Notices and Disclaimer
All Information contained in and produced by the ModernCalculators.com is provided for educational purposes only. This information should not be used for any Financial planning etc. Take the help from Financial experts for any Finace related Topics. This Website will not be responsible for any Financial loss etc.