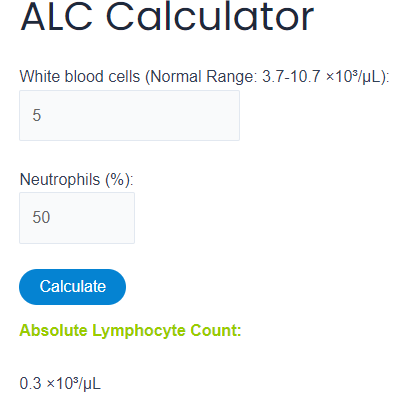
Introducing the ALC Calculator, the ultimate tool to help you monitor and manage your lymphocyte levels with ease. The ALC calc simplifies the process of understanding your ALC count, providing you with a clear, user-friendly interface to calculate and interpret your results. Make the most of this invaluable resource to ensure optimal immune function and overall health.
ALC Calculator
Absolute Lymphocyte Count:
0.3 ×10³/μL
[ez-toc]
What Are Lymphocytes?
Have you ever wondered how your body defends itself against harmful bacteria, viruses, and other threats? Meet the lymphocytes, your immune system’s tiny soldiers. These cells play a critical role in protecting your body and maintaining your overall health. In this article, we will explore what lymphocytes are, their types, functions, and why they are vital to your well-being.
What Are Lymphocytes?
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell found in the blood, lymphatic system, and various tissues throughout the body. They are responsible for identifying and eliminating foreign substances or pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells. In short, lymphocytes are essential components of your immune system that help your body fight off diseases and infections.
Types of Lymphocytes:
There are three primary types of lymphocytes, each with distinct roles in maintaining a healthy immune system:
- B cells: B cells, or B lymphocytes, are responsible for producing antibodies that target specific antigens (foreign substances). When a B cell encounters its specific antigen, it will multiply and produce large amounts of antibodies that neutralize the threat.
- T cells: T cells, or T lymphocytes, play a crucial role in cell-mediated immunity. They can be further divided into two main types: helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells. Helper T cells stimulate the immune response by releasing chemical messengers called cytokines. Cytotoxic T cells, on the other hand, directly attack and destroy infected or cancerous cells.
- Natural killer (NK) cells: NK cells are lymphocytes that can identify and kill abnormal cells without prior exposure to the foreign substance. They are particularly effective in detecting and eliminating virus-infected cells and cancer cells.
Functions of Lymphocytes:
Lymphocytes perform various functions to maintain a healthy immune system:
- Antigen recognition: Lymphocytes have the ability to recognize specific antigens, allowing them to target and eliminate the correct foreign substance.
- Immune response activation: Lymphocytes activate other cells within the immune system, such as macrophages and neutrophils, to mount a coordinated response against threats.
- Memory cell production: Some lymphocytes, known as memory cells, can remember previous encounters with a specific pathogen. If the same pathogen re-enters the body, these memory cells help to initiate a faster and more efficient immune response.
The Importance of Lymphocytes in Maintaining Health: Lymphocytes play a critical role in your body’s ability to combat infections and diseases. They ensure that your immune system functions effectively by identifying and eliminating harmful pathogens. Additionally, lymphocytes help maintain a delicate balance within the immune system, preventing excessive immune reactions that can lead to autoimmune disorders.
Lymphocytes are essential components of your immune system, working tirelessly to protect your body from harmful invaders. By understanding their types, functions, and importance in maintaining health, you can better appreciate the incredible work these tiny soldiers do to keep you safe and healthy. Make sure to prioritize a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep to support your lymphocytes and ensure a robust immune system.
Types of Lymphocytes in Details
Lymphocytes are the immune system’s cellular defenders, playing a vital role in maintaining your body’s health and well-being. These white blood cells recognize and neutralize harmful substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells. In this article, we will explore the different types of lymphocytes, their unique functions, and how they work together to keep your body safe from harm.
Three Main Types of Lymphocytes:
There are three primary types of lymphocytes, each with distinct roles in maintaining a healthy immune system:
- B cells (B lymphocytes) B cells are responsible for producing antibodies, which are specialized proteins that recognize and neutralize specific antigens (foreign substances). When a B cell encounters its specific antigen, it multiplies and differentiates into plasma cells and memory B cells. Plasma cells produce large amounts of antibodies that neutralize the foreign substance, while memory B cells persist in the body, providing a faster and more efficient immune response upon future encounters with the same antigen.
- T cells (T lymphocytes) T cells play a crucial role in cell-mediated immunity, a type of immune response that involves the direct action of immune cells. T cells can be further divided into several subtypes, including:
a. Helper T cells: Helper T cells, also known as CD4+ T cells, stimulate the immune response by releasing chemical messengers called cytokines. These cells help activate B cells, cytotoxic T cells, and other immune cells to mount a coordinated defense against pathogens.
b. Cytotoxic T cells: Cytotoxic T cells, also known as CD8+ T cells, directly attack and destroy infected or cancerous cells. They recognize and eliminate cells displaying abnormal or foreign antigens on their surface.
c. Regulatory T cells: Regulatory T cells, also known as Tregs, play a crucial role in preventing excessive immune reactions and maintaining immune tolerance. They suppress the activity of other immune cells, preventing autoimmune diseases and minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
d. Memory T cells: Like memory B cells, memory T cells provide long-lasting immunity by remembering previous encounters with specific pathogens. They enable a faster and more potent immune response upon subsequent exposures to the same pathogen.
- Natural killer (NK) cells NK cells are a unique type of lymphocyte that can identify and kill abnormal cells without prior exposure to the foreign substance. They are particularly effective in detecting and eliminating virus-infected cells and cancer cells. NK cells release chemicals called perforins and granzymes, which induce the targeted cell to self-destruct.
The various types of lymphocytes work together to protect your body from harmful invaders and maintain your overall health. By understanding the unique functions of B cells, T cells, and NK cells, you can better appreciate the incredible work these cellular defenders do to keep you safe. Prioritize a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep to support your lymphocytes and ensure a robust immune system.
Formula For Absolute Lymphocyte Count ( ALC Count)
The absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) is a vital component of your routine blood tests that can provide valuable insights into your immune system’s health. By measuring the number of lymphocytes in your blood, healthcare providers can evaluate your body’s ability to fight infections and detect potential underlying issues. In this article, we will discuss the formula for calculating the ALC, its clinical significance, and how to interpret your results.
Formula for Absolute Lymphocyte Count (ALC): The ALC is determined by multiplying the total white blood cell (WBC) count by the percentage of lymphocytes present in the blood sample. The formula for ALC is as follows:
ALC = (Total WBC count) x (Percentage of Lymphocytes)
The ALC is usually reported in cells per microliter (cells/µL) or cells per liter (cells/L). The normal range for ALC may vary depending on age, gender, and laboratory standards, but generally falls between 1,000 to 4,000 cells/µL or 1.0 to 4.0 x 10^9 cells/L.
Clinical Significance of ALC: The ALC is a vital parameter in assessing immune health, and its values can be indicative of various conditions:
- Elevated ALC: A high ALC can result from various factors, including viral infections, certain bacterial infections, or a heightened immune response. It can also be associated with conditions such as lymphocytic leukemia or lymphoma.
- Decreased ALC: A low ALC may indicate a suppressed immune system, which can be caused by factors like malnutrition, autoimmune disorders, or certain medications, such as corticosteroids and chemotherapy. A low ALC can also be a sign of bone marrow suppression or failure, HIV infection, or other immunodeficiency disorders.
Interpreting Your ALC Results:
It’s crucial to remember that ALC values should always be interpreted within the context of your overall health and other laboratory findings. If your ALC is outside the normal range, your healthcare provider will likely order further tests or evaluate potential underlying conditions to determine the cause.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy ALC:
To support your immune system and maintain a healthy ALC, consider the following lifestyle habits:
- Eat a balanced diet: Ensure your meals include a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats to provide essential nutrients that support immune function.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in moderate exercise to boost your immune system and overall health.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, as insufficient sleep can negatively impact your immune system.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, to support a balanced immune response.
The absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) is a key indicator of immune health, providing valuable insights into your body’s ability to combat infections and detect potential underlying conditions. By understanding the formula for calculating ALC and implementing healthy lifestyle habits, you can support your immune system and maintain optimal health. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your ALC or overall immune function.
Normal ALC Count Ranges And Levels
The absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) is a crucial parameter that helps evaluate the health and efficiency of your immune system. By understanding the normal ALC count ranges and levels, you can better assess your immune system’s ability to fight infections and detect potential issues. In this article, we will explore the normal ALC count ranges, factors that can affect these levels, and how to maintain a healthy ALC count.
Normal ALC Count Ranges and Levels: The ALC measures the number of lymphocytes (B cells, T cells, and NK cells) in your blood. The normal range for ALC may vary depending on age, gender, and laboratory standards, but generally falls between 1,000 to 4,000 cells/µL or 1.0 to 4.0 x 10^9 cells/L.
Factors Affecting ALC Levels:
Several factors can influence ALC levels, including:
- Age: Infants and young children typically have higher ALC levels than adults due to their developing immune systems. As people age, ALC levels may decrease slightly.
- Infections: Acute or chronic infections can cause fluctuations in ALC levels, with viral infections often leading to an increase in lymphocytes, and certain bacterial infections causing a decrease.
- Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and chemotherapy drugs, can lead to a decrease in ALC levels.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis can cause changes in ALC levels due to immune system dysregulation.
- Lifestyle factors: Poor nutrition, stress, and lack of sleep can also impact ALC levels and overall immune function.
Maintaining a Healthy ALC Count:
To support your immune system and maintain a healthy ALC count, consider implementing the following lifestyle habits:
- Eat a balanced diet: Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats to provide essential nutrients that support immune function.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to boost your immune system and overall health.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, as inadequate sleep can negatively impact your immune system and ALC levels.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, to help balance your immune response.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support overall health and immune function.
Understanding the normal ALC count ranges and levels is crucial for evaluating the health and efficiency of your immune system. By considering factors that can affect ALC levels and implementing healthy lifestyle habits, you can support a healthy ALC count and maintain a robust immune system. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your ALC or overall immune function.
If Levels of ALC Count Are High
A high absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) can indicate various health conditions or a heightened immune response. Understanding the potential causes and symptoms of elevated ALC levels can help you take appropriate steps to maintain a healthy immune system. In this article, we will discuss the possible reasons for a high ALC count, the symptoms you may experience, and the recommended management strategies.
Causes of High ALC Count:
An elevated ALC count can result from various factors, including:
- Viral infections: Common viral infections, such as the flu, mononucleosis, or hepatitis, can lead to an increased ALC count as your immune system mounts a defense against the invading virus.
- Bacterial infections: Certain bacterial infections, like tuberculosis or pertussis, can also cause a temporary increase in lymphocyte levels.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or celiac disease can trigger an overactive immune response, leading to elevated ALC levels.
- Lymphoproliferative disorders: An abnormally high production of lymphocytes can occur in conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), or lymphomas.
- Stress: Both physical and emotional stress can temporarily increase ALC levels as part of the body’s response to stressors.
Symptoms Associated with High ALC Count:
The symptoms you may experience with a high ALC count depend on the underlying cause. Some possible symptoms include:
- Fever, fatigue, and body aches: These are common symptoms of viral or bacterial infections.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes can result from infections, autoimmune disorders, or lymphoproliferative disorders.
- Joint pain and inflammation: These symptoms are often associated with autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Unintentional weight loss, night sweats, or frequent infections: These may indicate an underlying lymphoproliferative disorder.
Managing High ALC Count:
The management of a high ALC count depends on the underlying cause:
- Infections: For viral infections, rest and supportive care are typically recommended, while bacterial infections may require antibiotics.
- Autoimmune disorders: Treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response, as well as lifestyle changes to minimize symptom triggers.
- Lymphoproliferative disorders: Treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or stem cell transplantation, depending on the specific condition and disease stage.
- Stress: Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help regulate ALC levels and support overall health.
A high ALC count can result from various factors, such as infections, autoimmune disorders, or lymphoproliferative conditions. Understanding the potential causes and symptoms can help you take appropriate steps to manage elevated lymphocyte levels and maintain a healthy immune system. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your ALC count or overall immune function. They can guide you on the most suitable management strategies based on your individual circumstances.
ALC Calculator / ALC Count / ALC Calc can be used to know about it.Use above mentioned calculator.
If Levels of ALC Count are Low
A low absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) can be an indicator of a weakened immune system or an underlying health issue. Understanding the possible causes and symptoms of a low ALC count is essential for taking appropriate steps to support your immune system. In this article, we will discuss the potential reasons for a low ALC count, the symptoms you may experience, and the recommended management strategies.
Causes of Low ALC Count:
A reduced ALC count can result from various factors, including:
- Viral infections: Certain viral infections, such as HIV or hepatitis C, can lead to a decreased ALC count as they directly affect the immune system.
- Nutritional deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients, like zinc or vitamin B12, can contribute to a low ALC count.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can cause fluctuations in ALC levels due to immune system dysregulation.
- Medications: Some medications, like corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, or chemotherapy, can lead to a temporary or long-term decrease in ALC levels.
- Bone marrow suppression or failure: This can result from conditions like aplastic anemia or leukemia, where the production of lymphocytes is impaired.
Symptoms Associated with Low ALC Count:
The symptoms you may experience with a low ALC count depend on the underlying cause. Some possible symptoms include:
- Frequent or prolonged infections: A weakened immune system may struggle to fight off infections, leading to recurring or long-lasting illnesses.
- Fatigue and weakness: These can result from nutritional deficiencies, chronic infections, or bone marrow suppression.
- Swollen lymph nodes or spleen: These symptoms can indicate an autoimmune disorder or an underlying infection.
- Unexplained weight loss, night sweats, or bruising: These may suggest an underlying bone marrow disorder or malignancy.
Managing Low ALC Count:
The management of a low ALC count depends on the underlying cause:
- Infections: Treating the underlying infection, whether through antiviral or antibiotic medications, can help restore ALC levels.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Consuming a balanced diet and taking appropriate supplements can address deficiencies and support immune function.
- Autoimmune disorders: Treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response, as well as lifestyle changes to minimize symptom triggers.
- Medication-induced ALC reduction: Consult with your healthcare provider about alternative medications or dosage adjustments to minimize the impact on your immune system.
- Bone marrow suppression or failure: Treatment options may include growth factors, immunosuppressive drugs, or stem cell transplantation, depending on the specific condition and disease stage.
A low ALC count can result from various factors, such as infections, nutritional deficiencies, or medication side effects. Understanding the potential causes and symptoms can help you take appropriate steps to manage reduced lymphocyte levels and maintain a healthy immune system. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your ALC count or overall immune function. They can guide you on the most suitable management strategies based on your individual circumstances.
What Causes A High Lymphocyte Count?
A high lymphocyte count, also known as lymphocytosis, can be indicative of various health conditions or a heightened immune response. Understanding the potential causes of elevated lymphocyte levels can help you take appropriate steps to maintain a healthy immune system. In this article, we will discuss the possible reasons for a high lymphocyte count, the potential health implications, and the recommended management strategies.
Causes of High Lymphocyte Count:
An elevated lymphocyte count can result from various factors, including:
- Viral infections: Common viral infections, such as the flu, mononucleosis, or hepatitis, can lead to an increased lymphocyte count as your immune system mounts a defense against the invading virus.
- Bacterial infections: Certain bacterial infections, like tuberculosis or pertussis, can also cause a temporary increase in lymphocyte levels.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or celiac disease can trigger an overactive immune response, leading to elevated lymphocyte levels.
- Lymphoproliferative disorders: An abnormally high production of lymphocytes can occur in conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), or lymphomas.
- Stress: Both physical and emotional stress can temporarily increase lymphocyte levels as part of the body’s response to stressors.
Potential Health Implications:
A high lymphocyte count can have various health implications depending on the underlying cause:
- Infections: Elevated lymphocyte levels due to infections typically resolve once the infection has been treated or has run its course.
- Autoimmune disorders: A high lymphocyte count in autoimmune conditions can lead to inflammation and tissue damage if not properly managed.
- Lymphoproliferative disorders: In cases of leukemia or lymphoma, a high lymphocyte count may indicate disease progression or poor response to treatment.
Managing High Lymphocyte Count:
The management of a high lymphocyte count depends on the underlying cause:
- Infections: For viral infections, rest and supportive care are typically recommended, while bacterial infections may require antibiotics.
- Autoimmune disorders: Treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response, as well as lifestyle changes to minimize symptom triggers.
- Lymphoproliferative disorders: Treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or stem cell transplantation, depending on the specific condition and disease stage.
- Stress: Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help regulate lymphocyte levels and support overall health.
A high lymphocyte count can result from various factors, such as infections, autoimmune disorders, or lymphoproliferative conditions. Understanding the potential causes and potential health implications can help you take appropriate steps to manage elevated lymphocyte levels and maintain a healthy immune system. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your lymphocyte count or overall immune function. They can guide you on the most suitable management strategies based on your individual circumstances.
When to Worry About Low Lymphocytes
Low lymphocyte levels, also known as lymphocytopenia, can indicate a weakened immune system or an underlying health issue. Understanding when to worry about low lymphocytes and how to take action is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. In this article, we will discuss the potential concerns of low lymphocyte levels and the proactive steps you can take to support your immune health.
When to Worry About Low Lymphocytes:
Low lymphocyte levels can be concerning in the following situations:
- Persistent low levels: If your lymphocyte count remains low over time, this may indicate an ongoing health issue, such as a chronic infection, an autoimmune disorder, or bone marrow suppression.
- Severe lymphocytopenia: Extremely low lymphocyte levels can leave you more vulnerable to infections and may suggest a more serious underlying condition, such as HIV or leukemia.
- Frequent or severe infections: If you experience recurring or long-lasting infections, a low lymphocyte count may be impairing your immune system’s ability to fight off pathogens effectively.
- Additional concerning symptoms: Unexplained weight loss, night sweats, swollen lymph nodes, or persistent fatigue may point to an underlying condition that requires further investigation.
Taking Action for Low Lymphocyte Levels:
If you are concerned about your low lymphocyte count, consider taking the following steps:
- Consult your healthcare provider: Discuss your concerns and symptoms with your healthcare provider, who can evaluate your lymphocyte levels and determine if further testing or treatment is necessary.
- Monitor your health: Keep track of any infections or symptoms you experience, as this information can be helpful for your healthcare provider when assessing your immune health.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, getting adequate sleep, and managing stress can all contribute to a healthier immune system and may help improve your lymphocyte levels.
- Be proactive with infection prevention: Practice good hygiene, avoid close contact with sick individuals, and stay up-to-date on vaccinations to minimize your risk of infection.
- Address underlying causes: If an underlying health issue is identified, work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that addresses the root cause of your low lymphocyte count.
Low lymphocyte levels can be a cause for concern when they persist over time, are severe, or are accompanied by frequent infections or other concerning symptoms. By consulting with your healthcare provider, monitoring your health, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can proactively address low lymphocyte levels and support a robust immune system. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your lymphocyte count or overall immune function. They can guide you on the most suitable course of action based on your individual circumstances.
So, take advantage of the ALC calculator and make informed decisions about your immune health. By understanding your ALC levels and addressing any concerns or abnormalities, you can stay on the path to optimal well-being and enjoy a vibrant, healthy life.ALC Calculator / ALC Count / ALC Calc can be used to know your level.Use above mentioned calculator.